Electroslag remelting
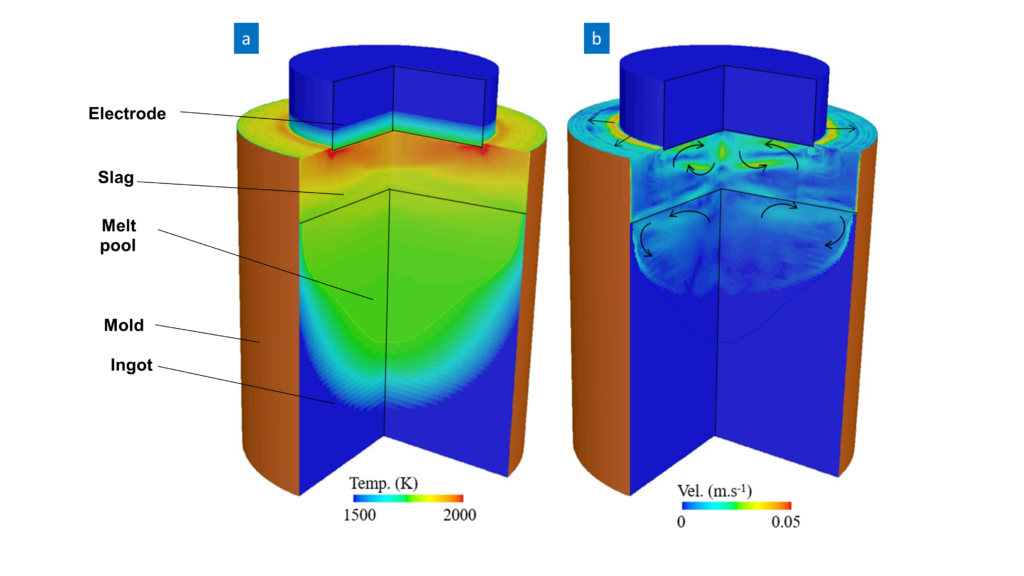
The Electroslag Remelting (ESR) is an advanced technology for the production of high quality materials, for example, hot work tool steels or nickel base alloys. In the past years, We developed several models aiming at predicting the way in which the operational parameters affect the structure and chemical composition of the final ESR ingot. Proper investigation of this process depends on the ability of the model to predict the Multiphysics resulting from the complex coupling between many physical phenomena. The process involves a range of physical phenomena and their interactions: heat transfer with phase change taking place in melting of the electrode and solidification of the ingot, chemical and electrochemical reactions in the slag, and the interaction between the turbulent flow and electromagnetic field known as magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). The main achievements to model the field of electromagnetism, fluid flow, heat transfer, and solidification are summarized in our publications. Additionally, our models address special topics in ESR such as prediction of the slag skin thickness and the mold current, melting and shape of the electrode, Non-metallic inclusion (NMI) in the ingot, electrochemical mass transfer through the slag, faradaic reactions at slag-metal interface, and multiphase aspects. The latter includes our direct numerical simulation (DNS) of the slag in ESR using VOF method to track the movement of slag-metal interface, and dripping of droplets through the slag.
The evolution of the shape of tip and melt rate of an electrode during electroslag remelting process considering the interactions between flow, temperature, and electromagnetic fields are modeled. The melt rate and shape of electrode tip reaches steady state.
Electroslag remelting (ESR) is a secondary metallurgical process aiming at further purification after completion of the primary extraction and refining operations. The process is a method of refining a consumable metal electrode through a molten slag that is electrically heated.
Transient 3D simulation of ESR reveals the turbulent chaotic flow field as shown in the animation.
Electroslag rapid remelting (ESRR) is the modified standard ESR process. A T-shape mold, with an embedded graphite ring to collect the electric current, is used. The key concept of ESRR is to combine the high production efficiency of continuous casting technique with the high ingot quality of ESR process. Transient 3D simulation of ESRR indicates the turbulent flow field as shown in the animation.
Publications
1) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Vakhrushev A., Wu M., Ludwig A., Bohacek J.: J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2021). DOI:10.1007/s42243-021-00686-z
“Investigation of effect of electrode polarity on electrochemistry and magnetohydrodynamicsusing tertiary curent distribution in electroslag remelting process”
2) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Wu M., Ludwig A., Bohacek J.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51 (2020) 871-879. DOI: 10.1007/s11663-020-01795-y
“A Numerical Investigation on the Electrochemical Behavior of CaO and Al 2O 3 in the ESR Slags”
3) Kharicha A., Karimi-Sibaki E., Wu M., Ludwig A., Bohacek J.: Steel Res. Int. 89 (2018) 1700100 1-20. D OI: 10.1002/srin.201700100
“Review on Modeling and Simulation of Electroslag Remelting”
4) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Wu M., Ludwig A., Bohacek J., Holzgruber H., Ofner B., Scheriau A., Kubin M.: Appl. Thermal Eng. 130 (2018) 1062–1069.
DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.100
“A multiphysics model of the electroslag rapid remelting (ESRR) process”
5) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Bohacek J., Wu M., Ludwig A.: Adv. Eng. Mater. 18 (2016) 224-30.
“On Validity of Axisymmetric Assumption for Modeling an Industrial Scale Electroslag Remelting Process”
6) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Bohacek J., Wu M., Ludwig A.: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 46 (2015) 2049-2061.
“A Dynamic Mesh-Based Approach to Model Melting and Shape of an ESR Electrode”
7) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Wu M., Ludwig A., Korp J.: Mater. Sci. Forum, 790-791 (2014) 396-401.
“Influence of crystal morphological parameters on the solidification of ESR ingot”
8) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Wu M., Ludwig A., Holzgruber H., Ofner B., Scheriau A., Kubin M., Ramprecht M.: Liquid Metal Processing & Casting Conf. (LMPC-16) (2017) pp. 213-216.
“CFD Modeling of the Electrode Change During the ESR Process”
9) Karimi Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Wu M., Ludwig A., Holzgruber H., Ofner B., Ramprecht M.: 2nd Int. Conf. Ingot Casting Rolling Forging, Milano, Italy, May 7-9 (2014) on data storage device.
“A parameter study on the effect of slag electrode conductivity on the solidification of a large scale ESR ingot”
10) Karimi-Sibaki E., Kharicha A., Wu M., Ludwig A., Holzgruber H., Ofner B., Ramprecht M.: Liquid Metal Processing & Casting Conf. 2013 (LMPC 2013) Sept. 22-25, Austin, Texas (2013) pp. 13-19.
“A Numerical Study on the Influence of the Frequency of the Applied AC Current on the Electroslag Remelting Process”
11) Kharicha A., Karimi Sibaki E., Wu M., Ludwig A.: Liquid Metal Processing & Casting Conf. 2013 (LMPC 2013) Sept. 22-25, Austin, Texas (2013) pp. 95-99.
“Contribution of the Mould Current to the Ingot Surface quality in the Electroslag Remelting Process”
12) Kharicha A., Körp J., Kubin M., Wu M., Ludwig A.: CLEANSTEEL8, Budapest, Hungary, 14-16 Mai 2012, pp 145-157.
“Investigations on the origin of radial distribution of non-metallic inclusions in ESR ingot”

